Ram Ddr2 In Slot Ddr3
DDR2 Vs. DDR3 will be the DDR RAM(Random Access Memory) variations where DDR3 is a more sophisticated version and is empowered with much more capabilities like high data transfer rate, low power consumption, memory reset choices, more memory, etcetera. Nevertheless, the principal difference lies inside the information speed where DDR3 provides double the rate provided by DDR2.
This difference in notch position is also why you can't use DDR3 RAM in a DDR2 system or install DDR2 RAM into a DDR3 slot (even though they have the same number of pins). In short, DDR2 and DDR3 RAM are not compatible with each other: If your motherboard has DDR2 RAM slots, then you can only use DDR2 RAM. The same applies to DDR3 RAM. As mentioned before, in regards to the memory settings both the DDR2 and DDR3 memory were set to AMD's maximum supported speeds of 1066MHz and 1333MHz respectively. I wanted to upgrade the RAM to 2 GB with a new installation of one 1 GB RAM, but I was also wondering if I can replace the old 1 GB DDR2 with a new 2 GB DDR3 RAM, and add one more 1 GB DDR3 RAM, making the whole RAM capacity to 4 GB DDR3. Please give me some thoughts. I think there have to be compatibility between the motherboard and the new. Computer Cables Yoton (M.2) B-Key SATA-Bus SSD to SATA 3.0 Adapter DDR Memory Slot Installation Motherboard Kit DDR2 DDR3 DDR4 DDR5 Desktop Mainbo - (Cable Length: 0.2m) Model #: B07R2BYSPD Item #: 9SIA9HJBZH1134.
With the development of technologies, the quicker versions of memories have been developed like DDR (Double Data Rate) memories. The major theory behind the DDR memories is that by employing row speech into the processor, a high number of bits are all obtained simultaneously within the processor.
There are many techniques used to raise the rate of the little transfer from hooks into the processor. The information is transported to the rising and falling edges of the clock; this is why these memories are referred to as Double Data Rate memory. Keep reading Colorfy’s article!
See also:
Table of Contents
Ram DDR2 vs DDR3 Definition
Bestseller No. 1Rambo: Last Blood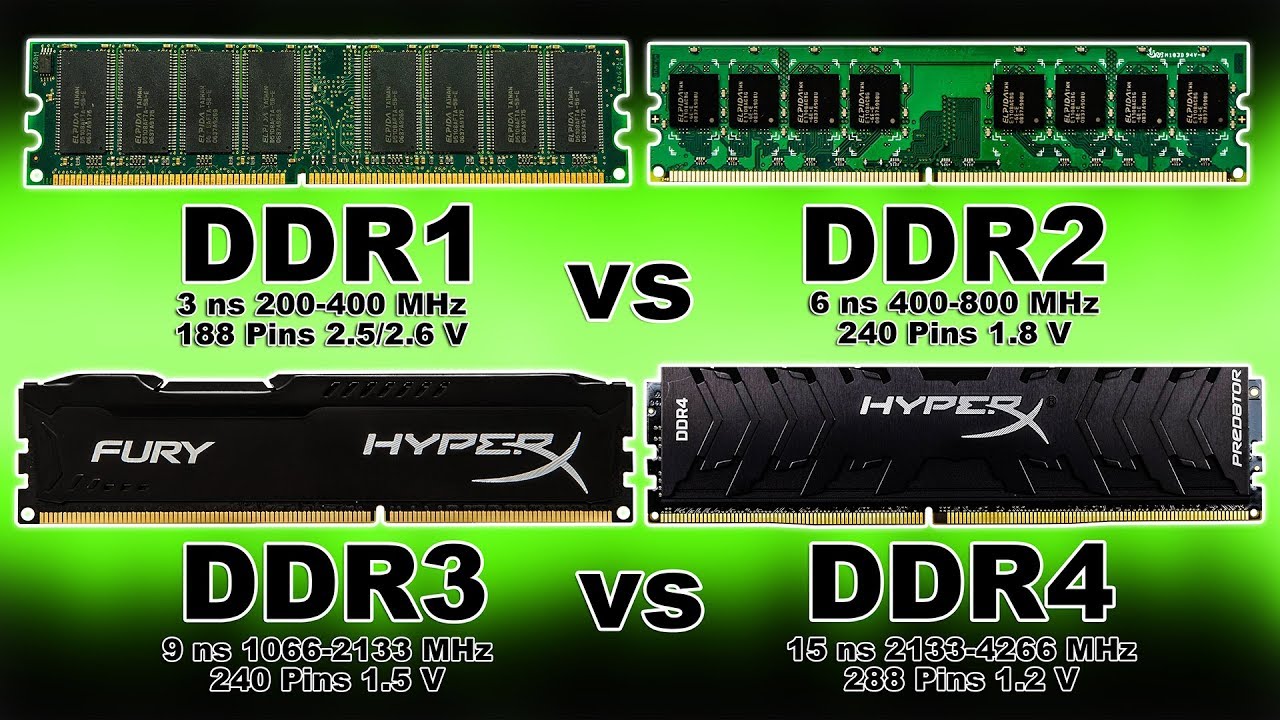 Rambo: Last Blood (Extended Cut)
Rambo: Last Blood (Extended Cut)What Is DDR2?
The DDR2 is the next version of the DDR (Double Data Rate) memories. These variations of this Random Access Memory was designed to reach a high data rate for its block-transferring. It can transfer information in the clock speed of 400 to 1066 Mhz.
The DDR two variant is the successor of the DDR in which the principal change is put on the operational frequency of the RAM chip and prefetch buffer along with also the amount of both of those parameters are increased. A prefetch buffer is a four-piece of memory cache, resides at the RAM chip of DDR2. The buffer is employed in the RAM processor for prepositioning the little from the data bus as quickly as possible.
DDR2 is a 240-pin DIMM structure that works at 1.8 volts. These DIMMs are made up of those one or more than one RAM processor in one board linked to the motherboard. The voltage of this DDR2 is decreased from the antecedent DDR technologies to get rid of the heat impact.
DDR uses 144 pin DIMM designs and works in the voltage of 2.4 volts. There’s not any compatibility between the DDR2 and DDR, as both utilize different motherboard socket and also DIMM keys.
What Is DDR3?
DDR3 is the advanced version of the DDR2 that has improved the prefetch buffer to 8 bits and the working frequency around 1600 Mhz. On the other hand, the sum of power has decreased to 1.5 volts, which also reduces the heat effect of this high frequency. The pin design of DDR3 also has 240 pins, but these cannot be utilized from the motherboard RAM of DDR2 due to the different notched key.
In DDR3 there’s an exceptional choice available for draining the memory via a software reset activity, i.e., memory reset. The memory reset alternative makes sure that the memory has been drained and vacant after rebooting the machine.
Benefits of DDR2 Vs DDR3 Ram
Higher bandwidth functionality, efficiently up to 1600 MHz: The principal advantage of DDR3 comes in the higher bandwidth made possible by DDR3’s eight pieces of massive prefetch buffer compared to DDR2’s 4-bit prefetch buffer or DDR’s 2-bit buffer.
DDR3 modules may transfer information in the sufficient clock speed of 800-1600 MHz with both falling and rising edges of a 400-800 MHz I/O clock. In comparison, DDR2’s current selection of robust data transfer rate is 400-800 MHz utilizing a 200-400 MHz I/O clock, and DDR’s scope is 200-400 MHz based on a 100-200 MHz I/O clock.
Greater performance at reduced power (longer battery life in notebooks ): DDR3 memory promises a power consumption reduction of 30% compared to current business DDR2 modules because of DDR3’s 1.5-V provide voltage compared to DDR2’s 1.8 V or DDR’s 2.5 V.
- Improved low power features
- Improved thermal layout (cooler)
Disadvantages of ddr2 and ddr3
DDR3 generally has greater CAS latency: While the common latencies for a JEDEC DDR2 apparatus were 5-5-5-15, the conventional latencies to the more recent JEDEC DDR3 apparatus are 7-7-7-20 for DDR3-1066 and 7-7-7-24 for DDR3-1333. DDR3 latencies are numerically higher since the clock cycles they’re measured are briefer; the real-time period is usually equivalent to or lower than DDR2 latencies.
Additionally, while all these are the criteria, manufacturing processes tend to improve with time. Finally, DDR3 modules will probably have the ability to operate at lower latencies compared to JEDEC specifications. It’s likely to locate DDR2 memory, which is quicker than the typical 5-5-5-15 rates, but it will take some time for DDR3 to collapse beneath the JEDEC latencies.
What is the Difference Between ddr2 v ddr3 RAM?
In the ddr2 ram vs ddr3 table, we can observe that DDR3 RAM provides better performance while consuming significantly less electricity.
The difference in clock rate and maximum transfer speed numbers seem impressive on paper. However, in reality, DDR3 RAM is just two to 10 percent faster than DDR2 RAM for most real-world software (based upon your hardware specification and utilization ).
Read also:Best RAM 2020: the top memory for your PC
ddr2 and ddr3 Conclusion
DDR2 is the earlier version and is obsolete technology, also DDR3 is a later edition of this DDR in which DDR3 has been improved and provides more features like an increased storage area, very low power consumption, platform flexibility.
Video: How to Identify RAM DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 and DDR4 from Motherboard Slots #170
Can You Use Ddr2 Ram In Ddr3 Slot
Last update on 2020-12-16 / Affiliate links / Images from Amazon Product Advertising API
How to identify computer ram ddr1 ddr2 ddr3, DDR4 Identifying the Computer RAM (Random Access Memory) like DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4 physically is not so hard if you follow the steps.
- Distance of Notch
- Integrated Chip (IC) type
DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4 is the most using RAM currently in the market.
First of all confirm is it DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, or Different DDR’s SDRAM. keep your DDR chip front-facing as given bellow. here look to the notch each DDR notch distance is different from others DDR. It’s mentioned in the picture.
Also Read :
Ram Ddr2 In Slot Ddr3 Price
Distance of Notch
- Notch Means above cuts Mark on RAM
- DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 having Single Cut mark on the base of the RAM
- But you can see the Cut mark (Notch) distance (see below photo)
- Notch of DDR1 and DDR2 are similar but if you see closely,
- You can find DDR1 Notch is just above the IC and DDR
- DDR2 Notch is just far to the IC
- Notch of DDR3 is different from the other two.
- Notch of DDR1 and DDR2 are similar but if you see closely,
- Notch Means above cuts Mark on RAM
Integrated Chip (IC)
- See the Above Photo
- DDR3 having small and square type IC.
- DDR2 is just bigger then DDR3 and smaller the DDR1,
- In this case, too, DDR1 and DDR2 are just a small difference
- IC in DDR1 are touched both top and bottom of RAM
- and IC in DDR2 is just center of the RAM
- See the Above Photo
Number of Pins in DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, DDR4
- DDR1 – 184 Pins
- DDR2 – 240 Pins
- DDR3 – 240 Pins
- DDR4 – 288 Pins
- DDR3 – 240 Pins
- DDR2 – 240 Pins
- DDR1 – 184 Pins
Voltage of RAM
- The voltage of RAM cannot be used for the Physical finding of RAM, but it can be used to place the RAM in the Motherboard Slot. (voltage are written in the RAM Slot of Motherboard)
- DDR1 Volts – 2.5 v
- DDR 2 Volts – 1.8 v
- DDR3 Volts – 1.5 v
- DDR4 Volts – 1.2v
- DDR3 Volts – 1.5 v
- DDR 2 Volts – 1.8 v
- DDR1 Volts – 2.5 v
- The voltage of RAM cannot be used for the Physical finding of RAM, but it can be used to place the RAM in the Motherboard Slot. (voltage are written in the RAM Slot of Motherboard)
- Click to Buy Best DDR RAMs for Desktops
- Click to Buy Best DDR RAMs for Desktops